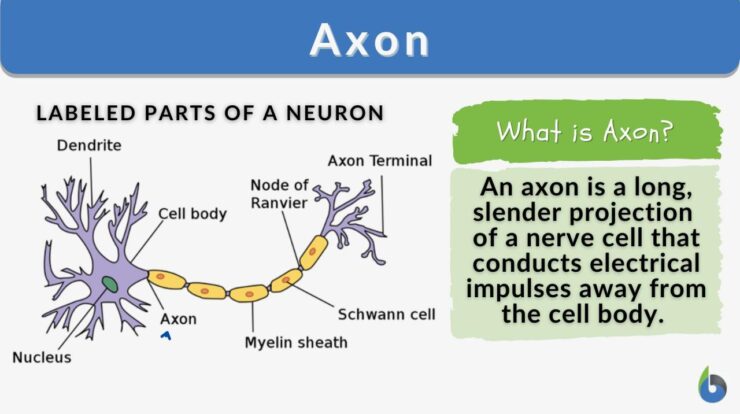
Cell language meaning, a concept that has captured the attention of scientists, holds the key to understanding the intricate communication network within our bodies. From genetic code to protein synthesis, cells employ a sophisticated language that governs their behavior and interactions.
This remarkable language enables cells to exchange vital information, coordinate functions, and respond to external stimuli, forming the foundation for tissue and organ function.
Cellular Language: Defining the Concept

Cell language refers to the complex system of communication and information exchange that occurs within and between cells. It encompasses a wide range of molecular mechanisms that allow cells to interpret, respond to, and transmit signals.
There are several types of cell languages, each playing a specific role in cellular function. Genetic language, encoded in DNA, carries the genetic code that determines the structure and function of proteins. Epigenetic language, involving modifications to DNA and chromatin, influences gene expression without altering the DNA sequence.
Proteomic language, involving the expression and modification of proteins, determines the functional state of the cell.
Cell Language and Communication
Cells communicate with each other using a variety of cell signaling molecules, such as hormones and neurotransmitters. These molecules bind to specific receptors on the surface of target cells, triggering a cascade of intracellular events that lead to a specific response.
Cell-to-cell communication is essential for tissue and organ function. It allows cells to coordinate their activities, respond to changes in the environment, and maintain homeostasis. Disruptions in cell communication can lead to a variety of diseases, including cancer and developmental disorders.
Translating Cell Language for Therapeutic Applications: Cell Language Meaning
Understanding cell language holds great promise for developing new therapies. By deciphering the molecular mechanisms underlying cell communication, scientists can identify potential targets for therapeutic intervention.
Challenges in translating cell language research into clinical practice include the complexity of cellular processes, the potential for off-target effects, and the need for personalized medicine approaches.
Despite these challenges, cell language is being used to develop targeted therapies for a variety of diseases, including cancer, autoimmune disorders, and neurological disorders.
Future Directions in Cell Language Research
Our understanding of cell language is still in its early stages. Current limitations include the lack of comprehensive maps of cell signaling pathways, the difficulty in studying dynamic cell-to-cell interactions, and the need for better computational tools to analyze complex datasets.
Emerging technologies, such as single-cell sequencing, spatial transcriptomics, and machine learning, are providing new insights into cell language. These approaches are helping to identify novel cell types, map cell-to-cell interactions, and decipher the molecular basis of cellular communication.
Future research directions include developing a comprehensive understanding of cell signaling pathways, investigating the role of non-coding RNA in cell communication, and exploring the potential of cell language for regenerative medicine.
Ending Remarks
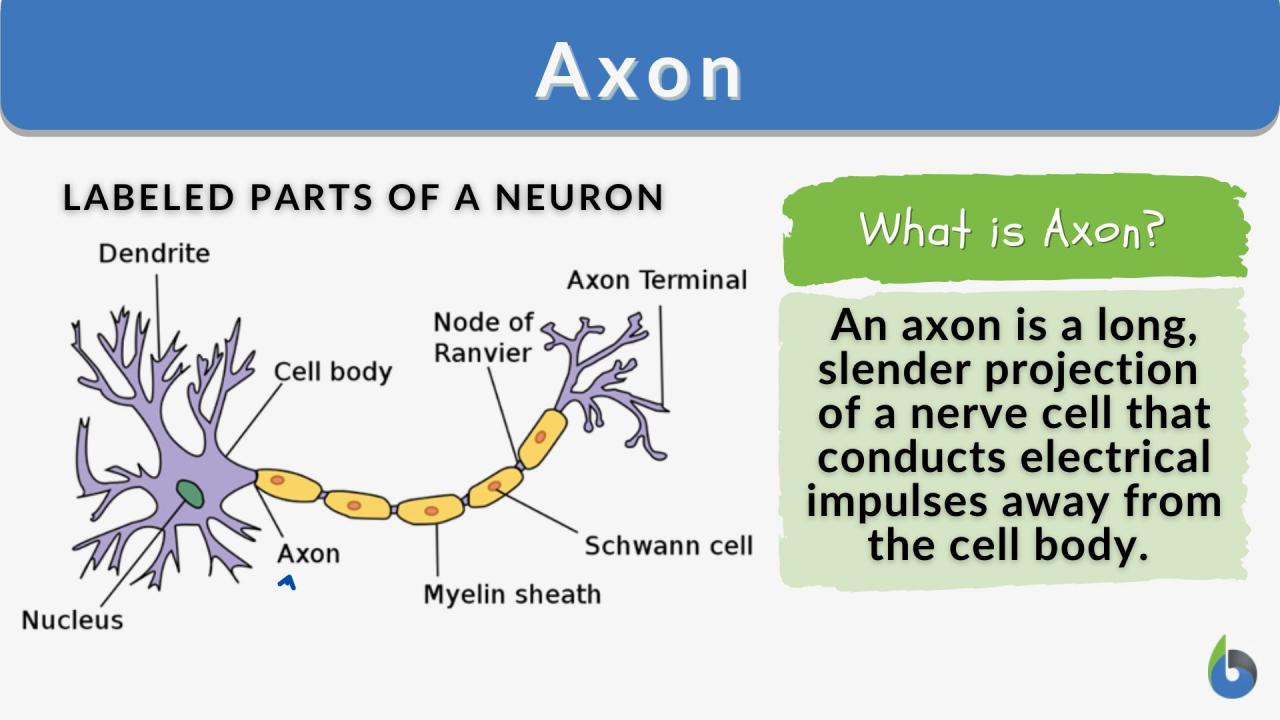
As we delve deeper into the complexities of cell language, we uncover a treasure trove of potential therapeutic applications. By deciphering the language of cells, we can develop targeted therapies that harness their natural communication pathways to combat disease and promote healing.
The future of cell language research promises exciting advancements, with emerging technologies and approaches paving the way for groundbreaking discoveries. This field holds immense potential to revolutionize our understanding of biology and transform the practice of medicine.
FAQ Section
What is the significance of cell language?
Cell language is essential for coordinating cellular functions, maintaining tissue integrity, and responding to external stimuli.
How do cells communicate with each other?
Cells communicate through a variety of mechanisms, including cell signaling molecules, direct contact, and gap junctions.
What are the potential therapeutic applications of understanding cell language?
Understanding cell language can lead to the development of targeted therapies that modulate cellular communication to treat diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders.





